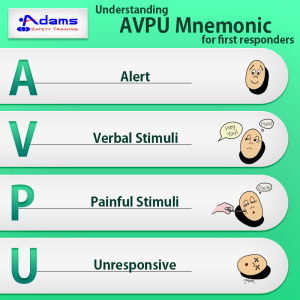
Most people, who experience sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) at home, work or in a public location, die because they don’t receive immediate CPR from bystanders at the site. As a first responder, now you can help a person in a SCA emergency with the help of this video. The video explains the two steps of hands-only CPR that can help rescuers save lives during SCA emergencies.
Hands-Only CPR is CPR without mouth-to-mouth breaths. The American Heart Association has recommended this CPR procedure for use in people who collapse suddenly in an ‘out-of-hospital’ setting. The two steps of Hands-Only CPR can increase the patient’s chance of survival. The two simple steps are: First – Call 9-1-1 and provide accurate information to the 911 dispatcher. Second – Provide chest compressions to the patient at a rapid rate of 100 compressions per minute. If the hands-only CPR technique is still not clear to you, check out this video to understand how to do this type of resuscitation.