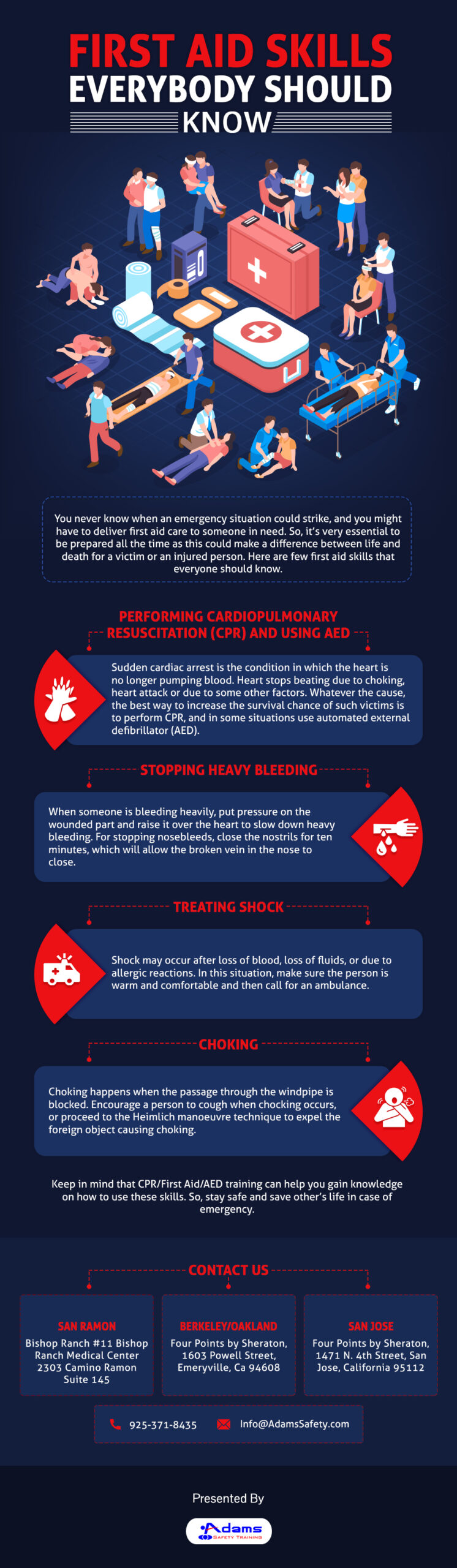
Introduction:
Accidents and injuries are a part of everyday life, and having a solid understanding of first aid can be invaluable in providing immediate care and minimizing the impact of common injuries. This comprehensive guide explores essential first aid techniques for addressing a range of common injuries. By equipping individuals with the knowledge to respond effectively, this guide aims to promote safety and well-being in various everyday situations.
1. Cuts and Lacerations:
- Assessing the Injury: Begin by assessing the severity of the cut or laceration. Apply gentle pressure to control bleeding, using a clean cloth or sterile dressing. If the bleeding is severe, elevate the injured area and seek professional medical help.
- Cleaning and Dressing: Clean the wound gently with mild soap and water to remove debris and reduce the risk of infection. Apply an antiseptic ointment and cover the wound with a sterile dressing or adhesive bandage. Monitor for signs of infection during the healing process.
2. Sprains and Strains:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE): Initially, encourage the injured person to rest and avoid putting weight on the affected area. Apply ice wrapped in a cloth to reduce swelling and pain. Use a compression bandage to provide support and minimize swelling. Elevate the injured limb to further reduce swelling.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers may be used to alleviate pain and inflammation. However, it is important to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional if necessary.
3. Burns and Scalds:
- Removing the Heat Source: Immediately remove the person from the source of the burn or scald. Cool the affected area under cool (not cold) running water for at least 10 minutes to reduce pain and prevent further damage.
- Dressing the Burn: For minor burns, apply a cool, sterile dressing or clean cloth to the affected area. Do not apply adhesive bandages directly to burns. Seek medical attention for more severe burns or if there is uncertainty about the severity of the injury.
4. Fractures and Broken Bones:
- Immobilization: Stabilize the injured area by using a splint or improvised materials such as a rolled-up newspaper or sturdy board. Apply the splint to the bone above and below the injury to prevent movement.
- Seek Medical Help: Fractures require professional medical evaluation and treatment. Call for emergency medical services and avoid moving the injured person unless necessary to prevent further injury.
5. Nosebleeds:
- Leaning Forward: Instruct the person to lean forward slightly to prevent blood from flowing down the throat. Pinch the nostrils together with gentle pressure and breathe through the mouth.
- Applying Cold Compress: Apply a cold compress or ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the bridge of the nose to help constrict blood vessels and slow bleeding. Maintain pressure for at least 10 minutes.
6. Eye Injuries:
- Avoid Rubbing: In the case of foreign objects in the eye, instruct the injured person to avoid rubbing the eye, as it may cause further damage.
- Flushing with Water: Gently flush the eye with clean water or sterile saline solution to remove any foreign particles. If the injury is more severe, cover the eye with a clean, sterile dressing and seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusion:
Having a comprehensive understanding of first aid for common injuries empowers individuals to respond promptly and effectively in times of need. By following the appropriate steps for cuts, sprains, burns, fractures, nosebleeds, and eye injuries, individuals can mitigate pain, prevent complications, and promote the healing process. It is important to remember that professional medical help should be sought for severe injuries or when there is uncertainty about the severity of an injury.
By familiarizing yourself with these first aid techniques, you can make a significant difference in providing immediate care to those around you. Remember to stay calm, assess the situation, and prioritize safety when responding to injuries. Additionally, consider taking a certified first aid course to further enhance your skills and stay up to date with the latest practices.
By being prepared and knowledgeable, you can play an essential role in safeguarding the well-being of yourself, your loved ones, and even strangers in critical situations. Remember, providing first aid not only relieves pain and promotes recovery but also gives peace of mind knowing that you can make a positive impact when it matters most.