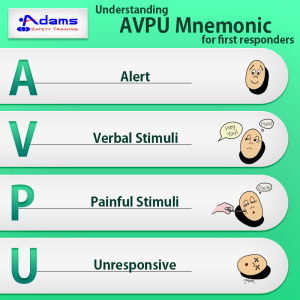
Taking a history from a patient suffering from acute or chronic pain is necessary for correct examination and providing medical care. To identify and characterize the pain symptoms, EMTs or doctors can use SOCRATES rule. SOCRATES is a mnemonic acronym used by emergency medical services and other health professionals to evaluate the nature of pain experienced by a patient following an accident.
• Site: Ask the patient where is the pain? What body part/parts are involved? By identifying the site of pain, you can easily make diagnostic decision.
• Onset: When did the pain start? Ask whether the pain is sudden, rapid or more gradual one.
• Character: Ask the patient to describe the pain. Is it sharp, dull, sore or stabbing?
• Radiating: Does the pain spread into other areas of the body? For example, if the pain is radiating from back to the arms and legs, then the patient may require surgery.
• Associated symptoms: It may happen that the patient experiences other symptoms such as nausea or vomiting with the pain.
• Timing: This is different from the onset of pain. Ask the patient when did he/she feel the pain most? Is it constant or does it happen at specific time of the day? Whether a certain movement is elevating the pain?

• Exacerbating and relieving factors: What makes the pain better or worse? Sometimes, certain physical position or medication can relieve the pain.
• Severity: The patient should be asked to give a number to the pain on a scale of 0–10, wherein 0 being the lowest and 10 being the most severe pain experienced. Emergency medical professionals with first aid and CPR certification are better able to use the SOCRATES rule in assessing pain.