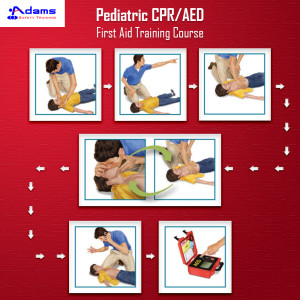
Seeing their own child in an emergency situation is a worst nightmare for parents. However, learning first aid and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) procedure can help parents act immediately and confidently in various emergencies.
First aid & CPR training for infants and young children is different than it is for adults. In a pediatric first aid/CPR course, participants learn how to recognize and respond to emergencies such as cardiac arrest and seizures; assess illnesses and respiratory problems; and treat wounds and burns in infants and young children. The best way to learn how to administer CPR or provide first aid to infants is to take a class that is approved by EMS authority or exempted. One can ask the local training provider to verify if the training program is certified and the program instructor is approved. Attending infant CPR/first aid courses is very important for parents & child care professionals because they can become a lifesaver for a child during a life-threatening situation. There are many benefits to being certified in first aid and infant CPR. See the below infographic to know why it is essential to enroll in an infant CPR training program.